Reduction of friction and wear on highly stressed components
Increase of the light absorption of metal surfaces through laser structuring (black marking)
Modification of the wetting behavior of surfaces through structuring
Functionalization of components through ultra-short pulse laser processing
The targeted modification of the surface topology of a material can completely change the functional properties of the component.
The structuring tool is always the same: the ultra-short pulse laser. The appearance and nature of the surface structures, however, can hardly be more diverse in the functionalization. The targeted laser structuring of running surfaces in plain or axial bearings can reduce the friction behavior between the components and thereby slow down wear.
Nanostructuring alters the wetting properties of surfaces, allowing them to exhibit hydrophilic or hydrophobic properties. A very rough surface absorbs the incident light in such a way that there is only a very low back reflection, the marking appears deep black.
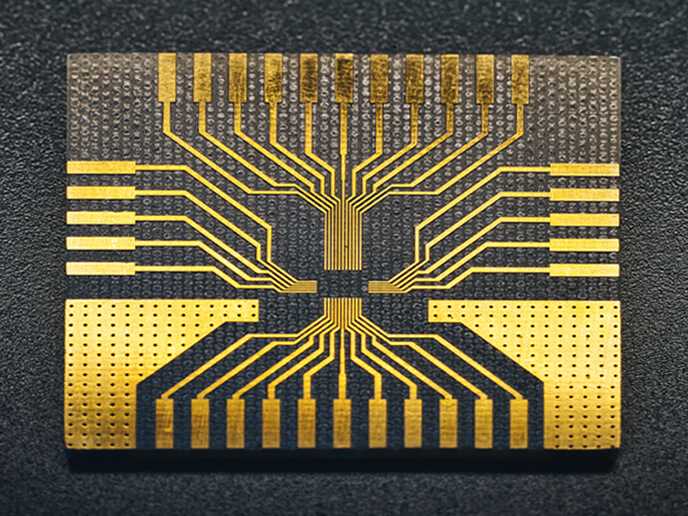
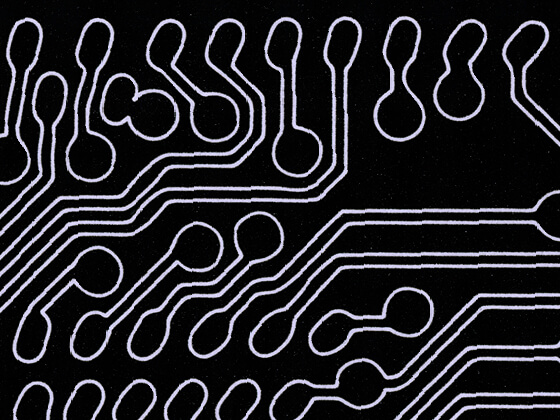
The functionalization of material composites, such as circuit boards, is also possible by a laser ablation with micrometer accuracy. For this purpose, the conductive material is precisely ablated by the laser process, without damagingthe carrier material (Ceramic, sapphire glass, FR4, or similar). Conductor tracks with different cross-sections and distances in the micrometer range can be produced.
Functionalizing surfaces: OUR STATISTICS
Realized reduction in friction
Production of conductive traces with a cross section of
Realized structure size for hydrophilicity/phobicity setting.
selective thin film ablation
Selective processing of thin layers
With ultrashort pulse lasers,thin film systems can be processed with high selectivity in all three spatial dimensions.
For example, metallized surfaces on a dielectric base substrate can be laser ablated with micrometer precision with insulation trenches and thus functionalized for applications in electronics and sensor technology.
With a suitable choice of the laser parameters, it is possible to remove the metallic surface without removing or significantly damaging the underlying base substrate.
Achievable qualities
- Lateral resolution : Typ. 20 μm, down to 1 μm
- Depth resolution : Typ. 100 nm, selective layer separation possible
Applications
- Sensors
- Electronics
- Solar cells
Surface functionalization Through nanostructuring
Nanostructuring of surfaces with the laser
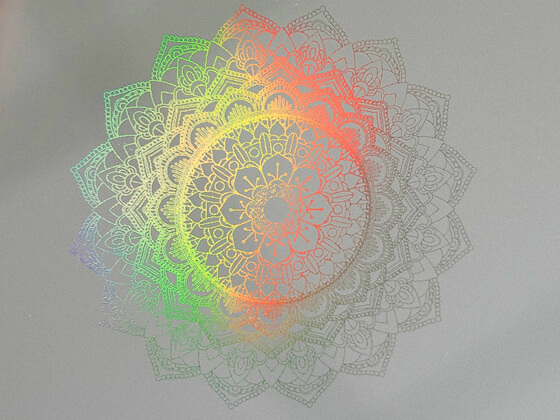
By using so-called laser interference structuring, nanostructures with a high area rate can be introduced into metallic, ceramic and plastic surfaces with the laser.
Thus, for example optically effective grid structures for product protection.
The technology also allows manufacture more antibacterial Surfaces.
The nanostructuring can do that Cell growth , the Adhesiveness and the Wetting can be specifically influenced by surfaces.
With the machine type RDX500, Pulsar Photonics offers laser machines for the industrialization of this technology.
Applications

All you need to know about surface functionalization
Learn more about laser micro processing
for industrial applications.
Resilient Markings
Markings for demanding environments
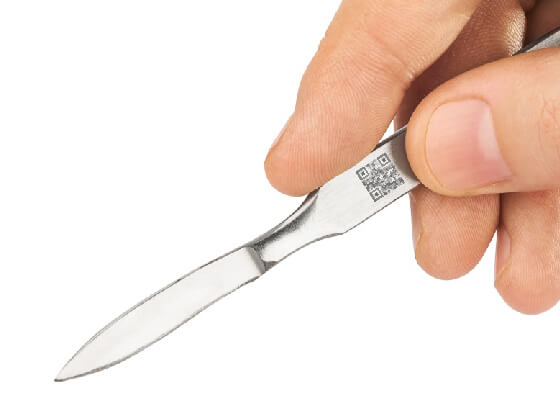
With ultrashort pulse lasers, corrosion-resistant , high contrast and abrasion-resistant markings in many metal components, especially stainless steel.
In contrast to conventional marking lasers, the marking is carried out by introducing a special microstructure.
The introduced microstructure has broadband light absorption properties, which leads to a high contrast with simultaneous abrasion resistance.
The chemical resistance of the marking is mainly due to the topography-related absorption mechanism used and, in the case of stainless steels, to the preservation of the protective effect against corrosion by a chromium oxide layer.
Applications

Your Personal Contact person
Dr. Marius Gipperich
Technical Sales